
이 글은 Paul Butcher의 Seven Concurrency Models in Seven Weeks을 읽고 작성했습니다
As Amdahl’s law starts to eclipse Moore’s law, a transition from object-oriented programming to concurrency-oriented programming is taking place.
ch1. introduction
Concurrent or Parallel?
통상 Concurrent는 동시성, Parallel은 병렬성으로 해석합니다
As Rob Pike puts it,
Concurrency is about dealing with lots of things at once. Parallelism is about doing lots of things at once.
concurrency는 여러개를 한번에 다루는것, parallel은 여러개가 한때에 진행되는 것을 의미합니다.
수업에서 학생이 읽는것을 들으면서, 반을 조용히시키고, 질문을 하는것은 concurrent 합니다. 만약, 보조 선생님이 한명 추가되어 같은 일을 하면 concurrent하고 parallel 하다고 할 수 있습니다.
concurrency나 parallelism은 전통적인 threads와 locks이 직접적인 parallelism을 지원하지 않기때문에 더 헷갈립니다. 멀티코어를 쓰레드와 락을 사용하고 싶다면, concurrent 프로그램을 작성해 parallel 하드웨어에서 돌리는 방법만 선택할 수 있습니다.
concurrent 프로그램은 종종 nondeterministic(비결정적)하기 때문에 불행합니다. 하지만 parallelism은 비결정적인 것을 도입하지 않아도 됩니다. 예를들어, array가 가진 숫자가 두배가 되는것은 비결정적인 것이 아닙니다. 프로그래밍 언어들은 비결정적이라는 공포를 도입하지 않아도 parallelism을 위해 특별한 지원을 할 수 있습니다.
병렬 아키텍처
Pararell Architecture
parallelism을 멀티 코어로 생각할 수 있지만, 현대 컴퓨터에선 parallel을 다양한 레벨에서 수행합니다.
비트 레벨
32bit 컴퓨터가 왜 8bit 보다 빠를까요? 8bit 컴퓨터가 32bit 숫자 두개를 더할려면 8bit 연산 연속이 필요할 것입니다. 반대로, 32bit가 8bit 숫자 두개를 더하려면 32bit에 포함된 4byte 각각으로 계산해 동시에 처리할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 64bit 아키텍쳐까지 왔지만, 이런 병렬성엔 제한이 있기 때문에 128bit 컴퓨터를 조만간 볼 순 없을것입니다.
명령어 레벨
pipelining, out-of-order execution, speculative excution으로 현대 cpu는 높은 병렬성을 지닙니다.
데이터 병렬성
SIMD, for “single instruction, multiple data” 이미지 처리에서 많이 사용, 현대의 GPU는 엄청나게 강력한 data-parallel 프로세서 입니다.
작업 레벨
가장 많은 사람들이 생각하는 병렬처리 단계입니다. 멀티 프로세서로 이루어집니다. 프로그래머의 관점으로 보면, 가장 구분되는 특징은 메모리 모델입니다. 공유 메모리 구조를 가지는가, 분산 메모리 구조를 가지는가의 차이가 있습니다.
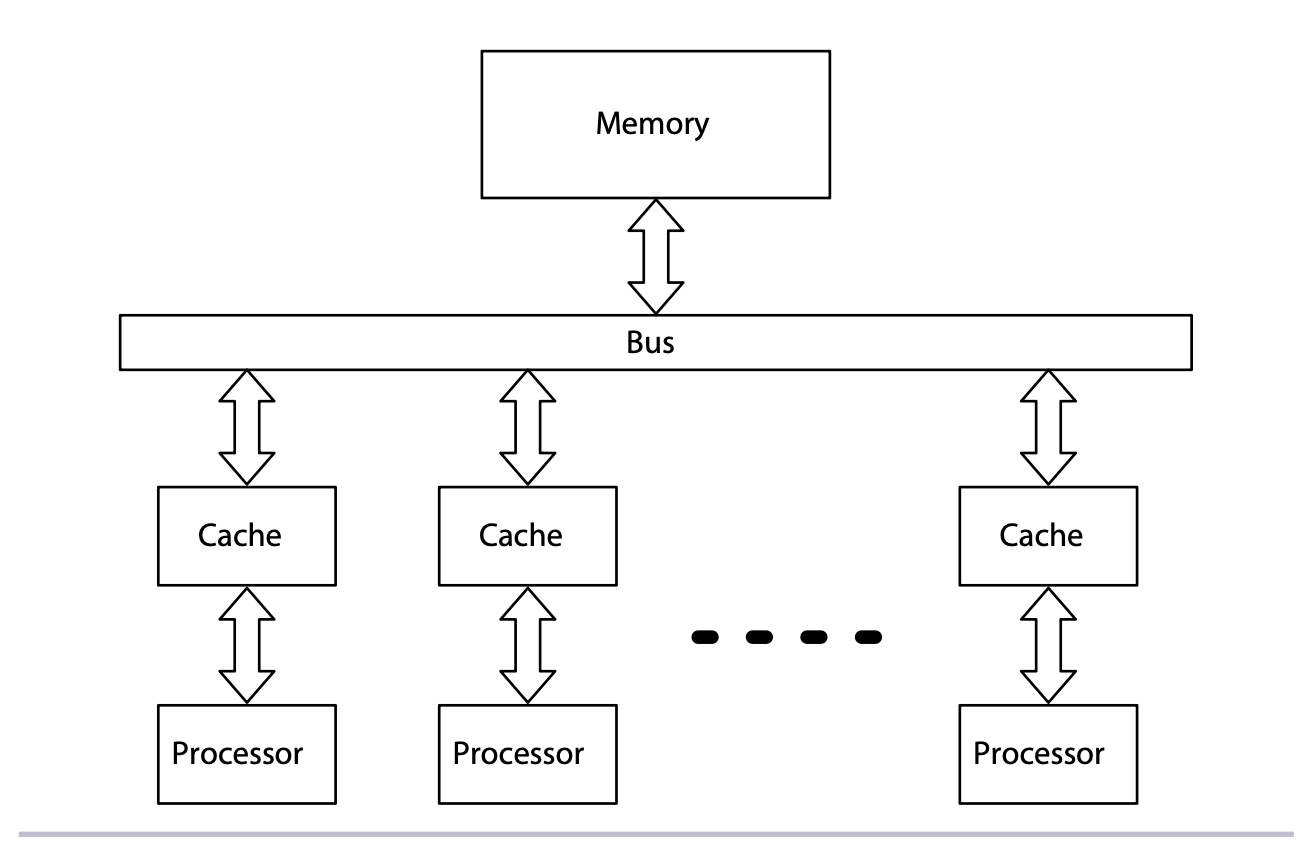
공유메모리를 통한 병렬성
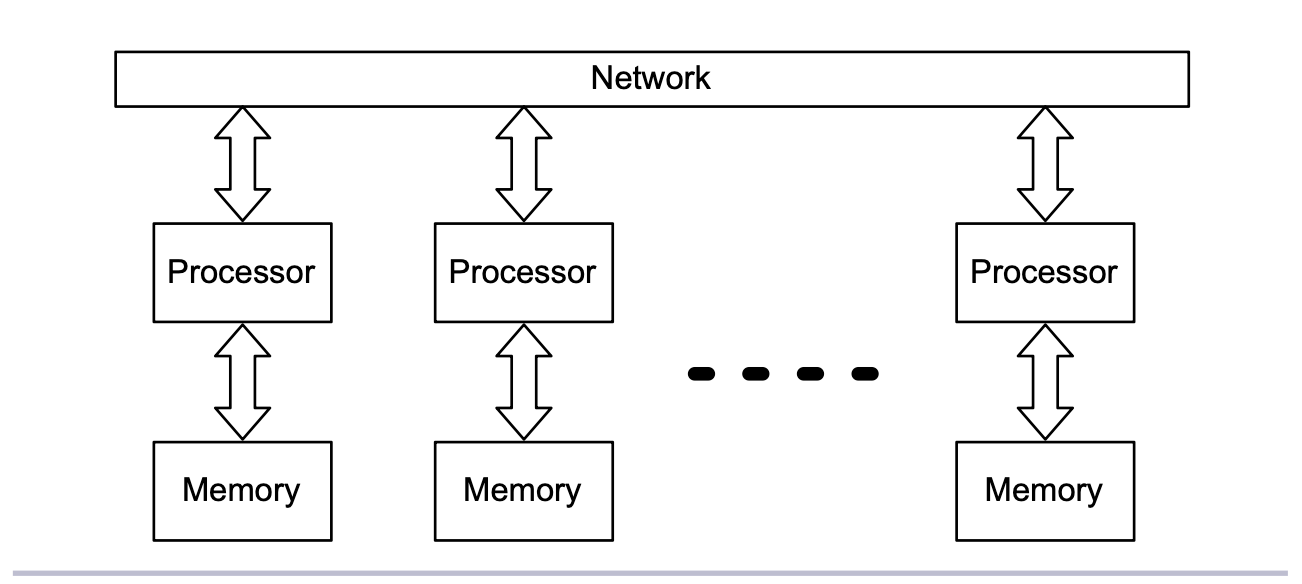
분산메모리를 통한 병렬성
동시성
Concurrency
동시성을 사용하면 더 responsive(반응적)하고, fault tolerant(오류 무결), efficient(효율적), simple(단순)합니다.
Concurrent Software for a Concurrent World
Concurrency is the key to responsive systems.
The world is concurrent, and so should your software be if it wants to interact effectively.
By downloading files in the background, you avoid frustrated users having to stare at an hourglass cursor.
Distributed Software for a Distributed World
distributing software helps it handle failure.
Sometimes geographical distribution is a key element of the problem you’re solving.
You might locate half your servers in a data center in Europe and the others in the United States, so that a power outage at one site doesn’t result in global downtime.
Resilient Software for an Unpredictable World
Concurrency enables resilient, or fault-tolerant
Independence is important because a failure in one task should not be able to bring down another.
Simple Software in a Complex World
it might be hard to believe, but a concurrent solution can be simpler and clearer
The extra work required to translate from the concurrent problem to its sequential solution clouds the issue. You can avoid this extra work by creating a solution with the same structure as the problem: rather than a single complex thread that tries to handle multiple tasks when they need it, create one simple thread for each.
일곱개의 모델
- thread and locks
- functional programming
- the clojure way
- actors
- communicating sequential processes
- data parallelism
- the lambda architecture
각 모델은 다른 장점을 지니고 있습니다. 앞으로의 챕터에서 다음 질문을 기억합시다.
- 모델이 동시성 문제를 해결하는지, 병렬성 문제를 해결하는지, 둘다인지
- 어떤 병렬성 아키텍처를 타깃으로 하는지
- 모델이 탄력적이거나 지리학적으로 분산된 코드 작성을 제공하는지

